Depression Treatment
Recognise the signs and find fast-acting, effective treatments for sustainable recovery.

Straight to:
It is estimated that 15% of the world’s population suffer from depression at some point in their lifetime and, in many cases, do not seek treatment. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) there are around 280 million people worldwide currently afflicted with depression. As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, a recent study estimates a staggering 27% increase in major depressive disorder worldwide.
Many sufferers have found antidepressant medications to be helpful and/or a form of ongoing psychotherapy with a trained mental health professional. In some cases, however, these interventions may not have worked, or the effects of the medications have worn off over time. Antidepressant medications may carry other unwanted side-effects such as weight gain, anxiety, loss of libido or sleeplessness.
In recent decades, outpatient neurostimulation techniques such as TMS and tDCS have come to the forefront as a way to treat depression without medications and can offer long-term sustained effects.
The use of psychedelics in medical controlled environments is also receiving growing interest and scientific backing, for the role it can play in helping patients with depression.
Often these treatments can be delivered in a relatively short time frame and because they target the underlying brain activity, the patient can experience more sustainable effects. These therapeutics are becoming appealing to many patients looking for relief from major depression, as they can be completed in a short space of time, with more promising outcomes.
What is Depression and who is affected
It is normal for people to experience mood swings and short-term negative emotions as a response to life's many challenges. A diagnosis of Major Depression, however, is a serious mental health condition that requires professional treatment and care. At its extreme and without the right support depression can be a life-threatening illness and can lead to self-harm.
To be classified as having depression, the person would be sad and experience a feeling of emptiness or a loss of interest for most of the day, every day, for a minimum of two weeks. They may also struggle to concentrate, feel hopeless about the future or display other symptoms, which we outline below.
Depression is rarely caused by one single factor. In most cases, sufferers develop depression because of a complex combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. Adverse life events like bereavement or unemployment make you more likely to develop depression. Medical professionals have also found that certain conditions like cardiac problems or sleep problems may lead to depression.
Women are twice as likely as men to suffer from depressive episodes, according to the National Institution of Mental Health (NIMH) and the WHO. The condition is found most commonly in younger people, but it can affect people of all age groups.
Symptoms of Depression
Here are common symptoms and feelings associated with depression:
Different diagnoses of depression
Clinical Depression
Clinical depression is a mood disorder that is characterized by a loss of life pleasure or a heavily depressed mood. When depression treatment is not undertaken in the right way, it may worsen and can be life-threatening. Clinical depression assessment must meet certain criteria as defined in the DSM-V, the diagnostic manual for psychological disorders.
Unipolar Depression
Unipolar depression is characterized by someone experiencing a low mood and negative feelings for a prolonged period.
Bipolar Depression
Bipolar depression is characterized by alternating periods in which a person feels depressive periods and subsequent periods of energy and activity.
Depression treatment methods
Antidepressant Medications
Antidepressant medications used today have been available since the 1950s. They have become a mainstay treatment for depression, however professional opinions on their effectiveness vary. Medications are shown to help with moderate, severe, and chronic depression.
Antidepressants work by relieving the symptoms of depression to help the patient feel a returned sense of emotional stability. They may also be used to prevent a relapse of depressive symptoms.
Like many oral medications, antidepressants can have side effects, which are often more noticeable at the beginning of the treatment. You may experience headaches, dizziness, dry mouth, weight gain, loss of libido and other side effects depending on the type of antidepressant.
At neurocare we are exploring the use of QEEG, a brain mapping technique used in our clinics, to help predict if a patient will respond to certain antidepressant medication. This may allow psychiatrists to better target and personalise treatment for depression.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy – also known as talk therapy - can be an effective treatment for depression. Psychotherapy can be delivered by a trained Psychologist, Psychiatrist, or other Medical Doctor. Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy have shown good results, but there are other evidence-based forms of psychotherapy that may be recommended and tailored to you.
Psychotherapy can help you adjust to difficult circumstances, and build awareness of thinking and behaviour. Together with your mental health professional, you will learn to identify negative behaviours and beliefs and workshop alternative perspectives and coping strategies. By "talking through it" with a professional, patients can regain a sense of confidence and an improved perspective or resilience to tackle everyday challenges.
For some patients who may need more acute intervention for Depression, Psychotherapy on its own may not be as effective or may take several months or years to reach an improved mindset. Often this bears a large and ongoing out-of-pocket expense to the patient. For faster effects, Psychotherapy can be integrated with other treatments like medication or Neurostimulation techniques like TMS. The dual effect can help boost progress and recovery in a shorter time frame.
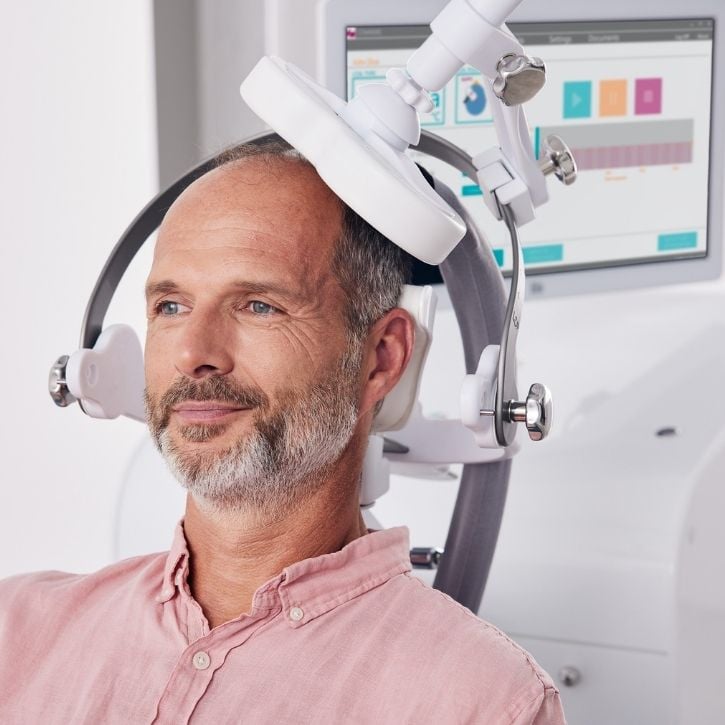
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Depression and depressive disorders can be treated effectively with a combination of psychotherapy and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). The benefits of magnetic stimulation are well-researched and scientifically proven as a treatment of depression. TMS can be fast-acting and may have minimal side effects. At neurocare, we combine TMS depression treatment with psychotherapy. Studies have found clinically significant improvements in two thirds of participants who had been treated with a combination of TMS and psychotherapy for major depression. Neurocare’s expertly trained clinicians can advise if this may be the right treatment for you.
Find a clinic
Seek innovative and personalized treatment at a clinic near you
How can TMS help with Depression
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a neurostimulation technique with fast antidepressant effects in as little as 20 sessions. For adults (18+) looking for a medication-free treatment for depression and anxiety disorders, TMS adjusts activity within brain networks that regulate our mood. Following neurocare’s leading protocols which combine TMS with talk therapy, studies show over two-thirds of individuals experience long-term positive effects with this approach.